Important links
Abstract
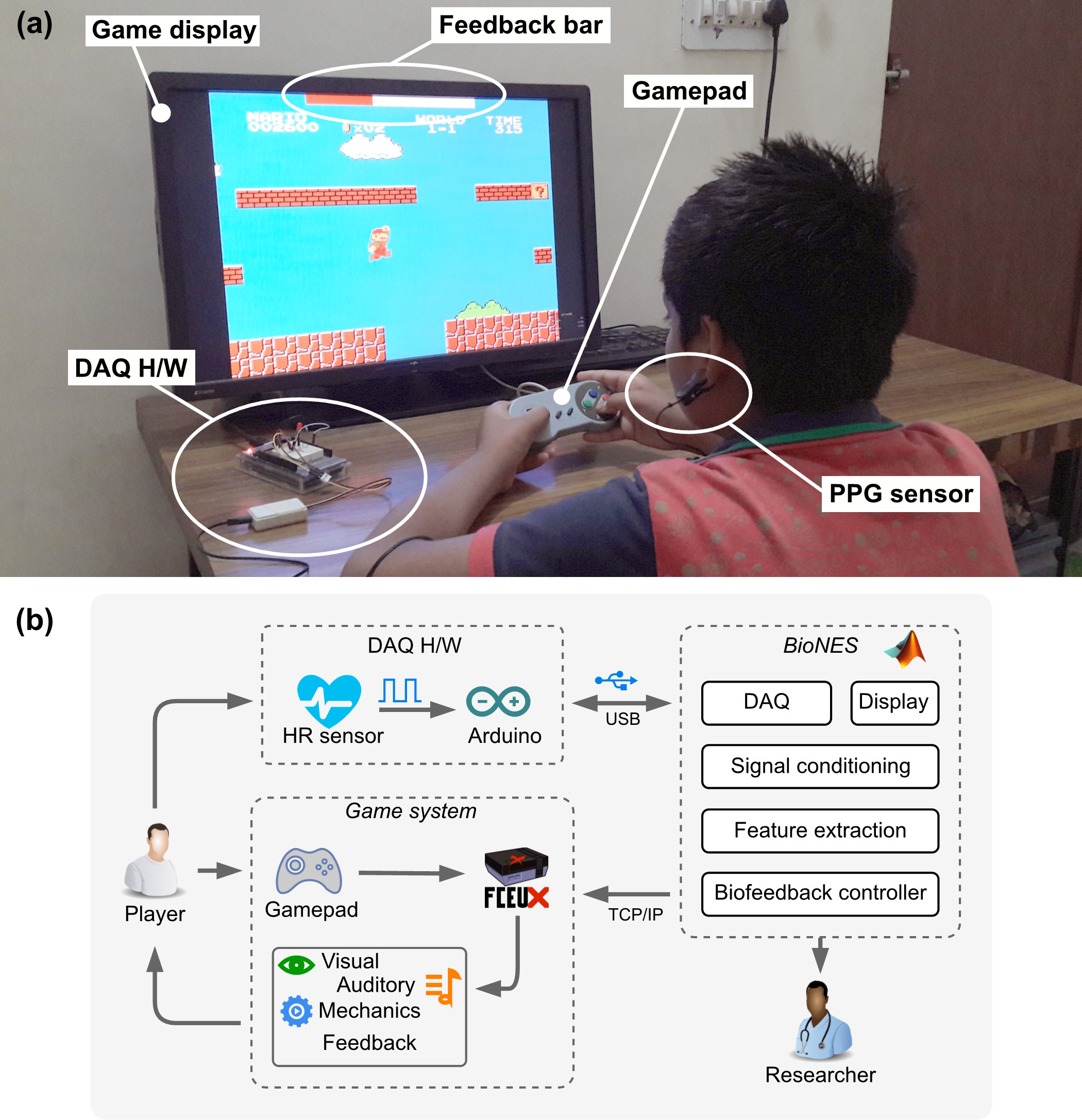
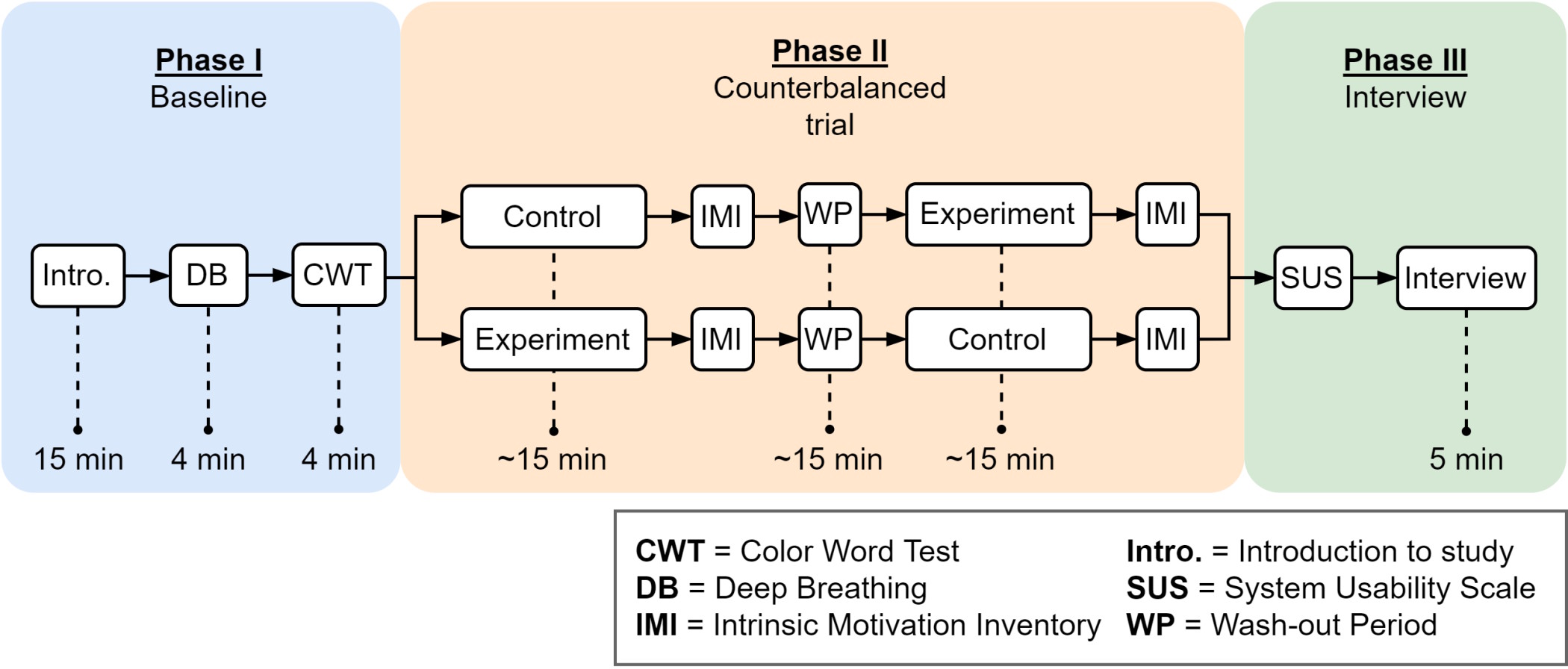
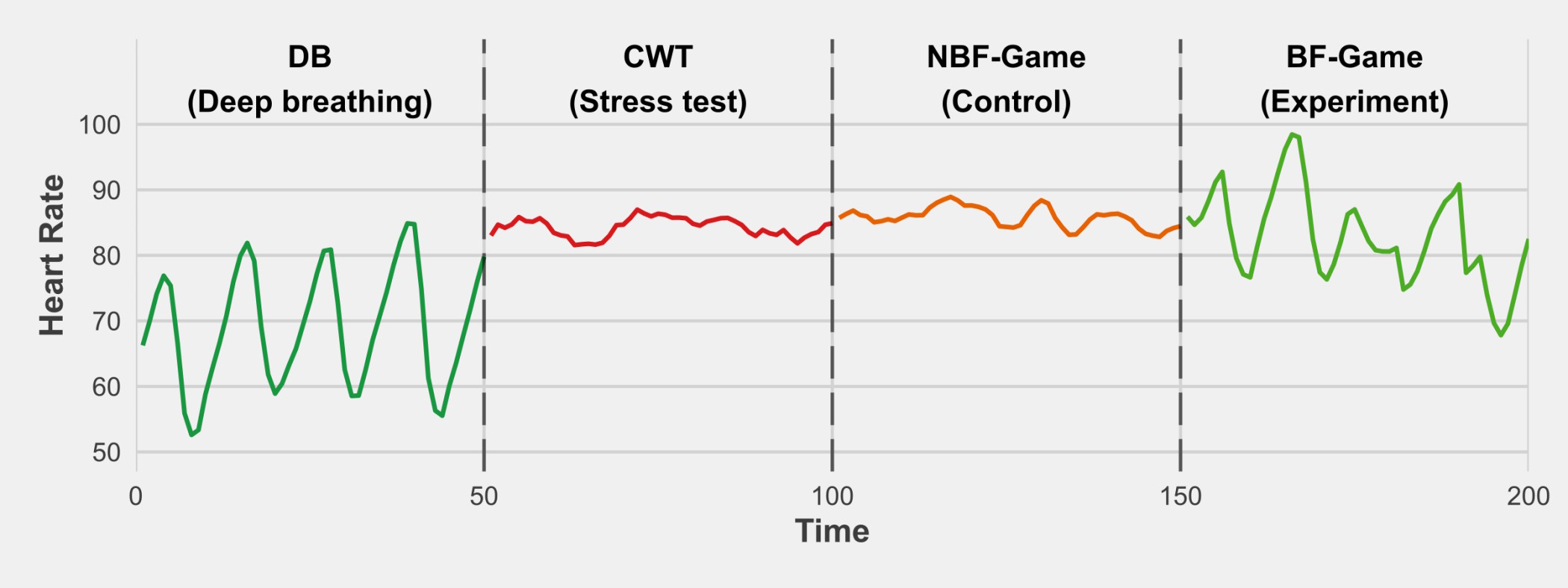
Video games are used to increase the engagement of biofeedback systems. For cost-effectiveness, the original Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) games can be used. Therefore, a multimodal biofeedback system was developed to leverage the NES games for biofeedback. This study aims to test the efficacy of the developed system, the motivation of participants, and the usability of the system. A within-group design study was conducted with 16 participants followed through four interventions: deep breathing, stress-test, non-biofeedback game (control), and biofeedback game (experiment), where their HRV was recorded. Participants showed significantly different HRV during interventions (F(1.60, 23.93) = 11.94, p < 0.001) and reported higher HRV when using biofeedback game than the non-biofeedback game (t(15) = 9.14, p < 0.0001). The motivation was reported to be the same with biofeedback and non-biofeedback version of the game, and the overall system was reported as usable. The results of this study support the efficacy of using original NES games in biofeedback for mental relaxation.
Important figures
Citation
@article{chand_efficacy_2022,
title = {Efficacy of {Using} {Retro} {Games} in {Multimodal} {Biofeedback} {Systems} for {Mental} {Relaxation}},
author = {Chand, Kulbhushan and Khosla, Arun},
doi = {10.4018/IJGCMS.295874},
journal = {International Journal of Gaming and Computer-Mediated Simulations (IJGCMS)},
year = {2022},
volume = {14},
number = {1},
pages = {1-23}}